Increase in Streaming Video Content
Internet browsing habits are increasingly visual and video content has taken off in a big way. In fact, Cisco’s Visual Networking Index Forecast predicts over 90 percent of all content on the Net will soon be in some form of video. Cisco also notes the incremental growth in Internet traffic between 2014 and 2015 at 17.2 exabytes per month. As a result of this growth in visual browsing habits, video has become a key component of content strategy.
There are significant challenges when creating quality video experiences and effective video streaming is dependent on several independent functions within a larger system. Broadly speaking, these independent functions include: compression technology, availability of bandwidth, and network infrastructure. If any single component within the system performs poorly, user experience of video streaming can be negatively impacted.
To ensure an optimized user experience involving video streaming, website administrators should implement streaming video monitoring. There are two steps involved with this process:
- Separate Video Streaming from other Network Elements: Typically, website traffic is identified by IP addresses and TCP/IP protocols. By themselves, these indicators are not enough because several web applications often use the same port. Hence, it is important to delineate and differentiate your video streaming traffic from other network traffic. This helps pinpoint problems with video streaming. In addition, it helps determine the need for additional bandwidth if the video quality deteriorates due to increased traffic.
- Test Video Streams: Video streaming can be deconstructed into a set of simple metrics that can be tracked using an appropriate monitoring solution. These metrics include buffering time (or the amount of time that it takes to buffer a video stream), frame rate (or the number of images that are being transmitted per second), and average bytes per second (or the rate at which bytes are being transferred).
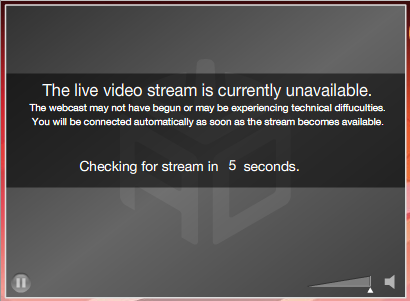
Monitoring Streaming Video
Streaming video monitoring connects to the media server, buffers appropriate content and plays the selected stream for 3-5 seconds. As a result of this process, it tests several metrics, such as Average Response Time, Connection time, Buffering Time, Received Packages, Buffering Packages, Frame Rate, Bitrate and Average Bytes per Second.
Dotcom-Monitor’s ServerView Video Monitoring has an integrated video streaming feature which checks video streaming services for performance and availability. ServerView is capable of testing several hundred formats (including standard formats: QuickTime, MP4, AVI, Flash, even mobile 3G2 (3GP2) & 3GP – see supported codecs here).
As the prevalence of streaming video increases, it is important to realize video streams are tied to user experience and content strategy – both key drivers of online business success. If you have identified the absolute path of your streaming media, you can run an Instant Streaming Media Test here. If you’d like to check web page performance and availability as a whole, you can run an Instant Browser Test here.

